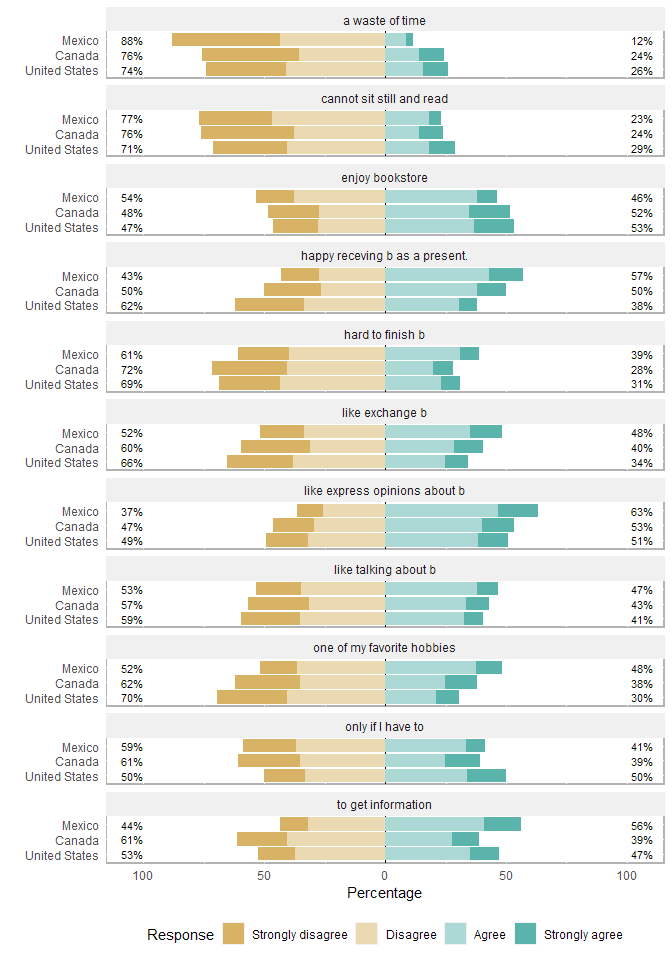Replace outdated snippets in this Old Revision?Yes No
Indice
Scale Likert
Il pacchetto Likert aiuta nella descrizione e nel trattamento delle scale di atteggiamento del tipo Likert.
Gli items devono essere fattori.
Vedi anche:
Pacchetti e dati
library(tidyverse) library(likert)
data(pisaitems)
Selezioniamo una sola scala come esempio:
items24 <- pisaitems %>% select_at(vars(starts_with("ST24Q")))
Per meglio comprendere i risultati, diamo un nome comprensibile agli items della scala:
# nomi degli items names(items24) <- c(ST24Q01="only if I have to", ST24Q02="one of my favorite hobbies", ST24Q03="like talking about b", ST24Q04="hard to finish b", ST24Q05="happy receving b as a present.", ST24Q06="a waste of time", ST24Q07="enjoy bookstore", ST24Q08="to get information", ST24Q09="cannot sit still and read", ST24Q10="like express opinions about b", ST24Q11="like exchange b")
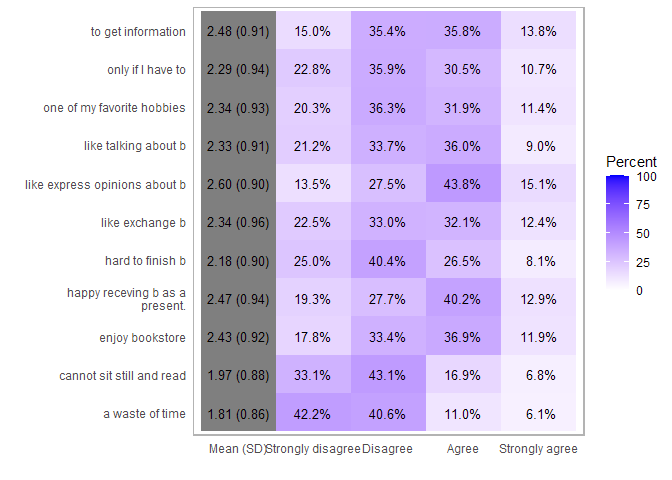
La funzione likert() organizza i risultati per tutti gli item di una scala:
likert(items24)
## Item Strongly disagree Disagree Agree Strongly agree ## 1 only if I have to 22.82298 35.90570 30.53855 10.732772 ## 2 one of my favorite hobbies 20.32308 36.32162 31.93453 11.420770 ## 3 like talking about b 21.24927 33.74201 35.96325 9.045464 ## 4 hard to finish b 24.95877 40.39249 26.50886 8.139890 ## 5 happy receving b as a present. 19.28187 27.65288 40.17350 12.891747 ## 6 a waste of time 42.24040 40.64689 10.97568 6.137024 ## 7 enjoy bookstore 17.84124 33.37107 36.88333 11.904361 ## 8 to get information 14.98106 35.41769 35.75990 13.841359 ## 9 cannot sit still and read 33.11719 43.12805 16.91875 6.836012 ## 10 like express opinions about b 13.53650 27.53867 43.82185 15.102982 ## 11 like exchange b 22.51850 33.02265 32.07993 12.378918
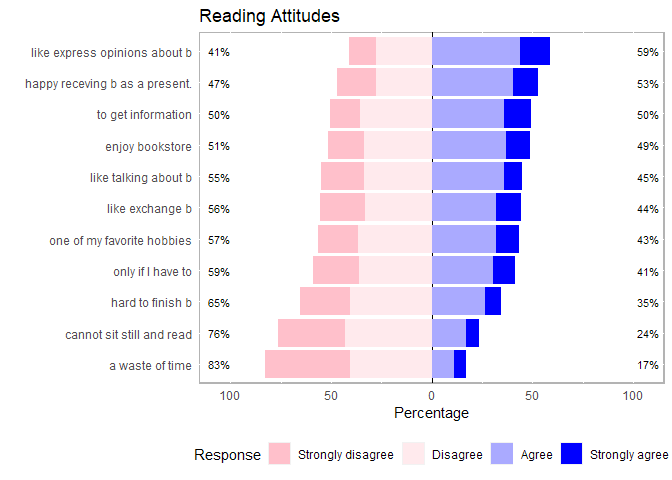
Statistiche descrittive
summary(l24)
## Item low neutral high mean sd ## 10 like express opinions about b 41.07516 0 58.92484 2.604913 0.9009968 ## 5 happy receving b as a present. 46.93475 0 53.06525 2.466751 0.9446590 ## 8 to get information 50.39874 0 49.60126 2.484616 0.9089688 ## 7 enjoy bookstore 51.21231 0 48.78769 2.428508 0.9164136 ## 3 like talking about b 54.99129 0 45.00871 2.328049 0.9090326 ## 11 like exchange b 55.54115 0 44.45885 2.343193 0.9609234 ## 2 one of my favorite hobbies 56.64470 0 43.35530 2.344530 0.9277495 ## 1 only if I have to 58.72868 0 41.27132 2.291811 0.9369023 ## 4 hard to finish b 65.35125 0 34.64875 2.178299 0.8991628 ## 9 cannot sit still and read 76.24524 0 23.75476 1.974736 0.8793028 ## 6 a waste of time 82.88729 0 17.11271 1.810093 0.8611554
Il centro (“neutral”) è pari a $(\text{nlevels}-1)/2 + 1$, (in questo caso = 2,5), ma può essere cambiato indicando un valore per l'argomento center, ad esempio:
summary(l24, center = 2)
Di default, gli item vengono ordinati per numero di rispondenti con punteggi alti.
Nota: Gli items “only if I have to”, “hard to finish b(ooks)”, “a waste of time”, “cannot sit still and read” hanno polarità invertita. Vedi Scale Likert: inversione delle polarità
Grafici
Il pacchetto permette di ottenere dei grafici immediatamente utilizzabili per la valutazione delle scale:
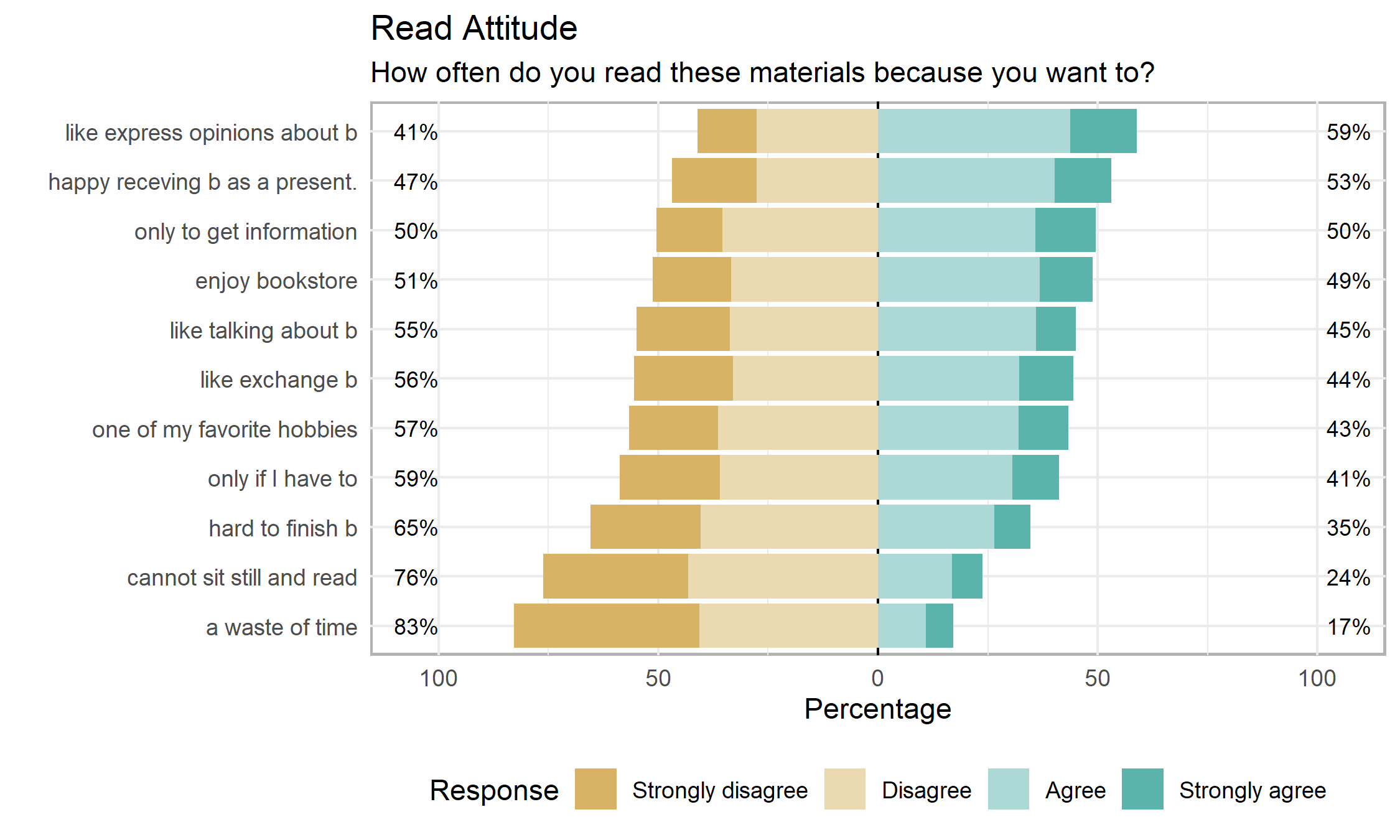
plot(l24)
# con colori e titolo col <- colorRampPalette(c("pink", "white", "blue"))(4) plot(l24, colors=col) + labs(title = "Reading Attitudes")
plot(l24, type='heat', wrap=30, text.size=3.5)
Variabili di raggruppamento
Nella funzione likert() è possibile indicare una variabile di raggruppamento:
l24g <- likert(items24, grouping=pisaitems$CNT)
summary(l24g) %>% head()
## Group Item low neutral high mean sd ## 1 Canada only if I have to 60.82666 0 39.17334 2.277647 1.0001779 ## 2 Canada one of my favorite hobbies 61.96628 0 38.03372 2.246538 0.9946381 ## 3 Canada like talking about b 56.91068 0 43.08932 2.274789 0.9467191 ## 4 Canada hard to finish b 71.77194 0 28.22806 2.054269 0.9211851 ## 5 Canada happy receving b as a present. 50.13961 0 49.86039 2.384124 0.9730841 ## 6 Canada a waste of time 75.72334 0 24.27666 1.944880 0.9748120
Dal momento che si tratta di un dataframe, possiamo selezionare nell'output le righe che ci interessano:
summary(l24g) %>% filter(Group == "Mexico")
## Group Item low neutral high mean sd ## 1 Mexico only if I have to 58.64345 0 41.35655 2.273828 0.8912875 ## 2 Mexico one of my favorite hobbies 51.68973 0 48.31027 2.435652 0.8726738 ## 3 Mexico like talking about b 53.23017 0 46.76983 2.372041 0.8832303 ## 4 Mexico hard to finish b 61.01569 0 38.98431 2.258031 0.8783913 ## 5 Mexico happy receving b as a present. 42.95741 0 57.04259 2.557262 0.9165585 ## 6 Mexico a waste of time 88.39568 0 11.60432 1.699286 0.7521860 ## 7 Mexico enjoy bookstore 53.62138 0 46.37862 2.385802 0.8478312 ## 8 Mexico to get information 43.57975 0 56.42025 2.605979 0.8836237 ## 9 Mexico cannot sit still and read 76.99317 0 23.00683 1.973779 0.8196108 ## 10 Mexico like express opinions about b 36.67250 0 63.32750 2.689749 0.8728100 ## 11 Mexico like exchange b 51.74623 0 48.25377 2.430137 0.9344254
La funzione non consente di cambiare l'ordinamento per le scale con gruppi, ma è possibile farlo a partire dal risultato:
summary(l24g) %>% arrange(Group, desc(high)) %>% head()
## Group Item low neutral high mean sd ## 1 Canada like express opinions about b 46.59327 0 53.40673 2.495512 0.9272673 ## 2 Canada enjoy bookstore 48.26595 0 51.73405 2.480138 1.0038762 ## 3 Canada happy receving b as a present. 50.13961 0 49.86039 2.384124 0.9730841 ## 4 Canada like talking about b 56.91068 0 43.08932 2.274789 0.9467191 ## 5 Canada like exchange b 59.59525 0 40.40475 2.238699 0.9930502 ## 6 Canada only if I have to 60.82666 0 39.17334 2.277647 1.0001779
Vedi le funzioni filter() e arrange()
I grafici:
plot(l24g, group.order=c('Mexico', 'Canada', 'United States'))
Altri esempi sono disponibili nelle demo del pacchetto.
Script di esempio
- es_Likert.R
library(tidyverse) library(likert) data(pisaitems) # selezioniamo una sola scala come esempio items24 <- pisaitems %>% select_at(vars(starts_with("ST24Q"))) # nomi degli items names(items24) <- c(ST24Q01="only if I have to", ST24Q02="one of my favorite hobbies", ST24Q03="like talking about b", ST24Q04="hard to finish b", ST24Q05="happy receving b as a present.", ST24Q06="a waste of time", ST24Q07="enjoy bookstore", ST24Q08="to get information", ST24Q09="cannot sit still and read", ST24Q10="like express opinions about b", ST24Q11="like exchange b") likert(items24) l24 <- likert(items24) str(l24) summary(l24) ## # qui non ha senso, perché le alternative sono solo 4 ## summary(l24, center = 2) summary(l24) %>% LabRS::kabbit(digits = 2, col.names = c("Item", "basso", "neutro", "alto", "media", "sd"), caption = "Statistiche riassuntive: output" ) plot(l24) # con colori e titolo col <- colorRampPalette(c("pink", "white", "blue"))(4) plot(l24, colors=col) + labs(title = "Reading Attitudes") plot(l24, type='heat', wrap=30, text.size=3.5) # variabile di raggruppamento l24g <- likert(items24, grouping=pisaitems$CNT) summary(l24g) %>% head() summary(l24g) %>% filter(Group == "Mexico") summary(l24g) %>% arrange(Group, desc(high)) %>% head() plot(l24g, group.order=c('Mexico', 'Canada', 'United States'))